History
Cytogenetic Division
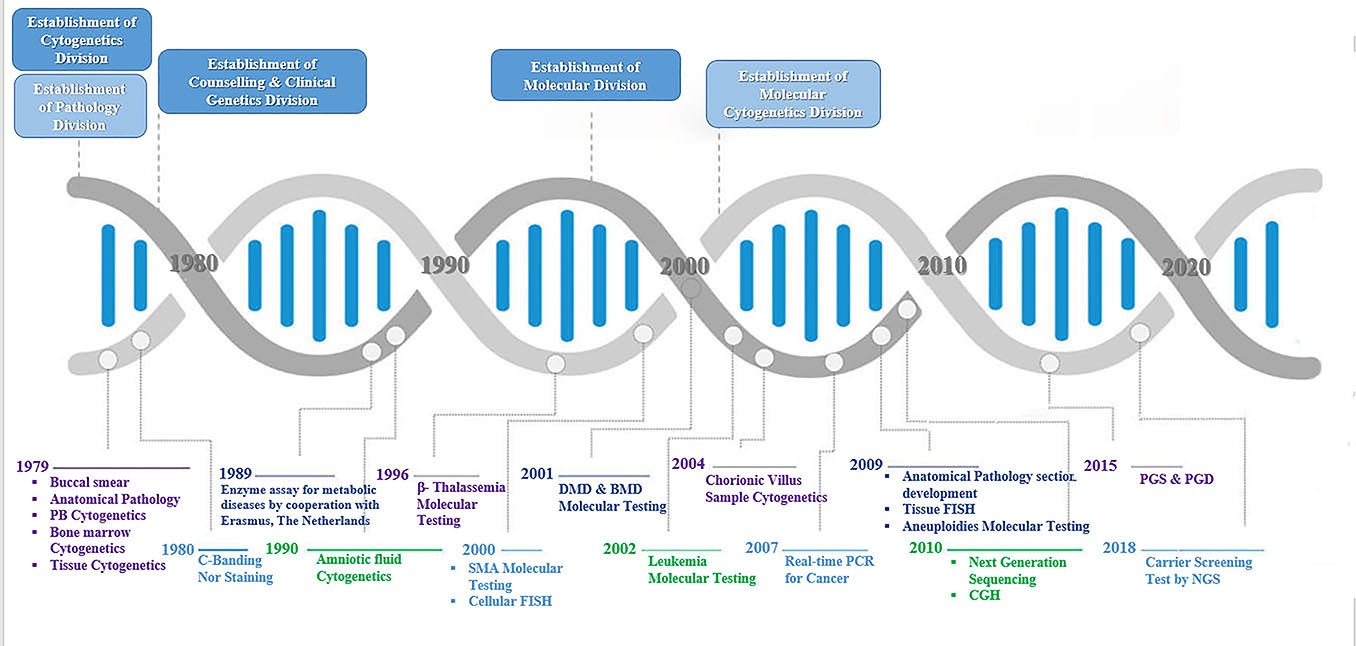
After successfully setting up the chromosomal staining (G-banding) methodin 1979 at Masoud Laboratory,Professor Mohammad Hassan Kariminejadestablishedwhat is now the Kariminejad-Najmabadi Pathology & Genetics Center. From itscommencement, this Center provided diagnostic cytogenetics services on peripheral blood and buccal smear samples. Soon after establishment of this Center,bone marrow samples were accepted, followed by bone marrow culture and tissue culture,then the C-banding technique and nucleolus organizer region (NOR) stainingwere added to the list of laboratory services. In less than 3 months, this Center was able to provide amniotic fluid cultures and prenatal diagnoses. At that time, establishing prenatal diagnosis in Iran needed more courage and power , because of increasedlegal restrictions on selective termination of an affected fetus and funding not being covered by insurance. In the first year after beginning prenatal diagnosis, only 17 samples were collected, while now this has reached 8000 samples annually. Taking samples, culture and karyotyping of chorionic villus samples commenced in 2004, toreducesample turnaroundtime and for high risk pregnancies.
Counseling Division
The Counseling Division was active from the beginning of the establishment of the laboratory in 1980, and counseling was provided by Professor Kariminejad. In 1997,Dr Yousef Shafeghati, a pediatrics geneticist, started to visit the patients especially for metabolic disorders.
Some other physicians were gradually added to our counseling teamincluding Dr Navid Almadani,Dr Fariba Afroozan, as well as Dr Bita Bozorgmehr (pediatrician), and many articles have been published in peer-reviewed journals by these members of staff.
In 2007, Dr Ariana Kariminejad, the second child of Professor Kariminejad, guidanceof her father and Doctor Shafeghati, became Director of the Counseling Division.
The Counseling Division has developed over time and now includessix physicians and three masters. Our Center is playing an active role in fostering collaborative relationships with other Iranian and international scientific and diagnostic organizations, while focusing domestically on integrating best practices and sharing lessons learned.
Molecular Genetics Division
In 1996,Professor Hossein Najmabadi joined the Center and set up the Molecular Genetics Division, which completed the diagnostic services of the Center. Professor Najmabadi is a leader in establishing developmental molecular techniques for the detection of inheritable genetic disorders. He set up several molecular genetic tests using the latest molecular techniques.He established the genetic analysis of common hereditary diseases in Iran which, previouslyhad beenvery expensive to diagnose, including thalassemia, Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophies (DMD/BMD), Fragile X syndrome (FRX), Y microdeletion and infertility in men. The most important activities of Professor Najmabadi were the establishment of the new molecular multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) technique for the detection of genomic deletions and duplications as well as developing Quantitative Fluorescence Polymerase Chain Reaction (QF-PCR) as an inexpensive, rapid and reliable method for prenatal recognition of numerical chromosomal abnormalities. Hewas a pioneerin establishing the Sanger sequencing method for detection of known single gene disorders in Iran from 2006, which benefits a huge number of families affected by such disease. He has also played an active role in the development of genetic tests for Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF), cystic fibrosis (CF), Fanconianemia, retinoblastoma, and polycystic kidney disease(a list of diseases and genes is available on our web page “Tests”).
The most reliable and convenient assays provided by this center are cancer diagnostics as well as predictions of cancer therapies, which help to increase our understanding about the tumor’s characteristics, evaluate a patient’s overall prognosis, and determine the best treatment options.
By applying high throughput, massively parallel sequencing (MPS or next generation sequencing, NGS) technology,recently developed in the last4 years, this division has enhanced the diagnostic capabilities for the first time in the country. Initially, different panels were used for single gene diagnostics, but subsequently, Whole Genome Sequencing (WES) and targeted generation sequencing using multiple diagnostic panels for over 4000 genes were set up. Recently, the Molecular Genetics Division has applied methods for mutation detection in somatic cells for various types of cancers including the KRAS/NRAS StripAssay and Sequencingfor which many patients have been referredto undergo this diagnosis from all over the country.Our Center is renowned as a referral center for these kinds of tests in Europe, as itcomplies withrigorous international standards.
Molecular Cytogenetic Division
In 2007, the Molecular Cytogenetic Division of this center started its work by providing Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) services on amniotic fluid samples. In 2008, for the first time in the country, the division established Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) and Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS) techniques and soon thereafter the Bac array and Oligo array CGH techniques. In 2009, the FISH service was provided on tissue samples, in addition to increased development of this division for PGS equipment. In an effort to establish the position of the SNParray in routine clinical practice, we are introducing a new diagnostic tool based on amniotic fluid and chorionic villus samples.
Pathology and Cytology Division
Since its foundation in 1979, the main focus of the Pathology and Cytology Division of Kariminejad-Najmabadi Pathology & Genetics Center was anatomical pathology services, includingsurgical, post-mortem pathological, and cytological examination, on fetal samples (autopsy, placental pathological investigation), and gynecological specimens (related to specializing in the female reproductive system). By developing the anatomical pathology section in 2009, the division gained the ability to provide molecular pathology services as well as covering the needs of both molecular and cytogenetic divisions in this regard. The present services offered by this division include post-mortem exams (fetal, newborn autopsy, placental pathology), pathological diagnosis of different types of excisional biopsies, immunohistochemistry (IHC), FISH for tissue samples, clg-FISH;preparing suitable samples for cancer molecular tests, as well as other molecular tests, and providing histological glass slides and tissue blocks.
In 2009, the clinical pathology section started to work in this multidisciplinary division, and is active in the field of counseling, the diagnosis of genetic and metabolic diseases in the fetus and newborn through laboratory screening, as well as providing various cancer diagnostics.
International Collaboration
From its foundation, this Center believed in unlimited knowledge boundaries, and the principleof providing equality of medical resources and opportunities for all people, undertaking an active role in fostering collaborative, synergistic relationships with the most important clinical organizations in Europe and Asia, and if necessary with USA, and in the case of rare diseases,collaborating with international facilities for accurate diagnoses; for example, successful collaboration with King’s College London, UK in 1989 to establish prenatal diagnosis for thalassemia,and with Erasmus University, Rotterdam, The Netherlands for the investigation of metabolic disorders.